The remarkable future of industrial automation: introducing virtual commissioning.

Commissioning is an enduring methodology that can be based entirely on the use of simulation to test and optimize manufacturing systems prior to their physical construction.
Some insights into a key catalyst for advancing digital transformation in the context of manufacturing and industrial processes.
The notion of virtual commissioning
Virtual commissioning represents a breakthrough in the approach to manufacturing. Its main mission is to simplify the setup process, reduce costs, improve efficiency and enhance factory output through the use of advanced simulations. Not only does this methodology help meet Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT) deadlines in project plans, but it goes further by enabling “virtual FAT” in some cases.
Overcoming traditional challenges
Traditional set-up and start-up challenges, are often the cause of delays and additional costs in industrial projects. They are addressed by modern manufacturing simulations. The historical failure to test control software until the hardware is physically completed is overcome, radically changing the sequence of project implementation.
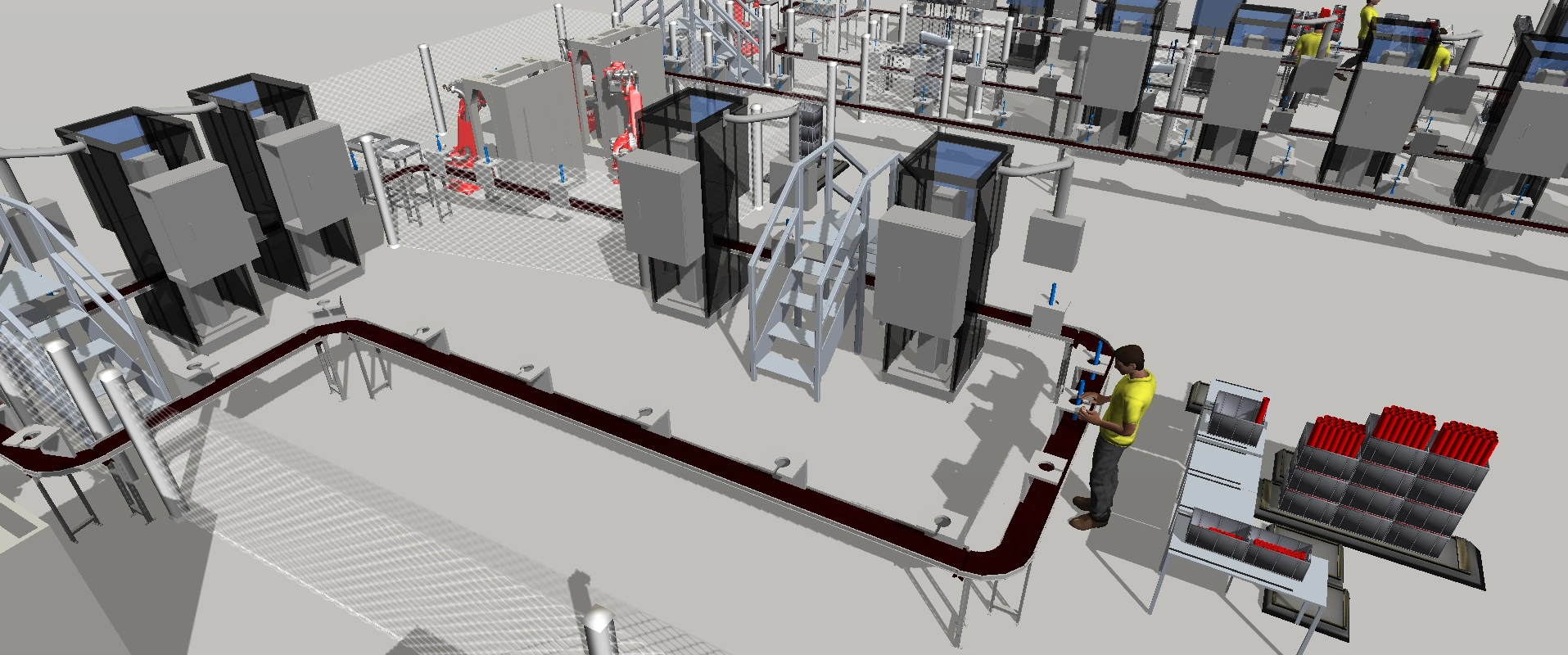
Software and commissioning: the heart of the process
With the advent of the programmable logic controller (PLC), software has risen to the driver’s seat in the field of automated machinery and equipment. However, until a few years ago, tests could only be performed on physical machines, inevitably delaying the commissioning process.
Virtual commissioning reorders this sequence, reducing the impact of commissioning on the critical path of the project. Creating a static representation of the machine using 3D CAD data, adding kinematics and a control system, was the first step towards virtual testing of the control software.
Most recently, with the advent of the fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0), it became possible to create “smart” manufacturing systems that can alert their status, react to trends and optimize performance with very little human intervention.
The complexity of systems introduced by Industry 4.0 has required new processes to facilitate their implementation and oversee their operation. Two of these processes are digital twin and virtual commissioning.
Digital twin is based on the virtual reconstruction of a physical system. A computer model enables the exchange of data between the virtual and real systems. Digital twins can replicate single machines, cells and production lines or even entire factories.
Virtual commissioning is aimed at simulating the control logic and signals that eventually enable an automation system to run, so as to replicate its operation and complete its controls. In fact it is considered a key element in staying ahead of competitors and maximizing return on investment.
The pressure to rapidly implement new Industry 4.0 technologies also makes this methodology an indispensable strategic tool.
The captivating benefits of virtual commissioning
The benefits of virtual commissioning are numerous and highly visible. Early detection of problems, reduced project execution time, significant financial savings, and increased design flexibility are just some of the positive impacts.
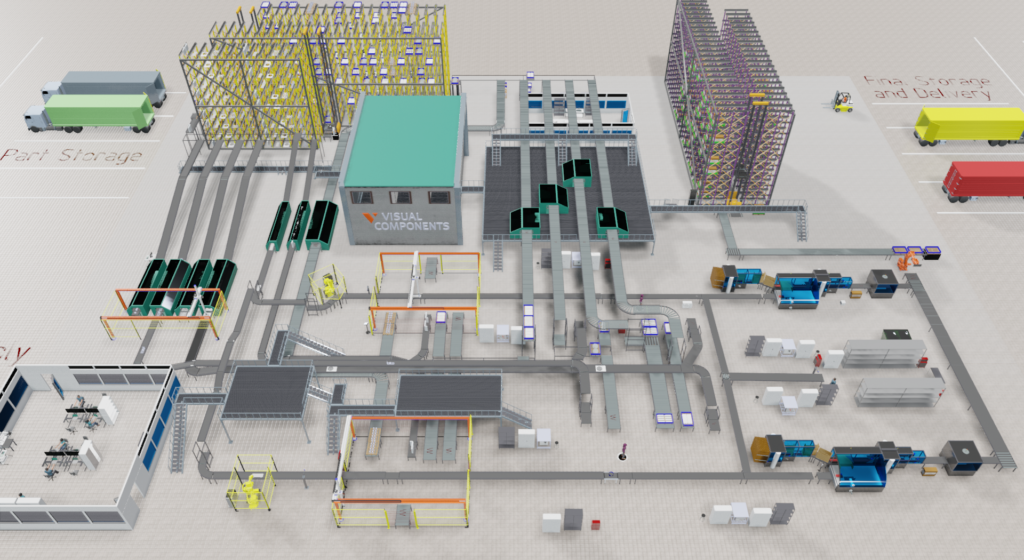
In essence (a step-by-step walkthrough of the virtual commissioning process):
Virtual commissioning is revolutionizing the way manufacturing plants systems are tested and optimized before they go physically into service. Enterprises in every industry can maximize the benefits of this innovative practice with a collaborative operating model developed within the company or by integrating external parties and teams. Some crucial stages for best practices:
Clear understanding is the starting point. A well-informed and knowledgeable team avoids mistakes by ensuring that virtual commissioning provides useful and applicable real-world data.
Analysis and definition of goals and production system functionality should be ensured by gathering essential documentation and requirements. This phase lays the foundation for a virtual model that is true to reality.
Building the 3D model is the next step, which is initiated from CAD data. With tools such as Flexsim and Visual Components, an extremely accurate 3D model can be created. Integration of kinematic data will provide a detailed representation of the designed equipment.
Logics can then be integrated by connecting the PLC and robot controller to the digital model in order to test sequences and system behavior. The connectivity of our simulation software with different manufacturers ensures an cross-compatible approach.
Simulation and testing are the next step. The model should be subjected to diverse operational scenarios, testing performance under both normal and error conditions. This step ensures that the system will effectively handle unexpected events.
After commissioning, it is key to adopt an approach of continuous improvement. Virtual commissioning reduces the need for physical startup. After this stage, feedback can be gathered to further refine the control model and logic. This ensures that processes are dynamic and constantly evolving. This system enables continuous improvement and immediate responses to rapid changes imposed by the markets.


Combining mechanical design and software development for industrial system automation, even the most complex, is a sure path to innovation.
It enables the enhancement of the quality of services and products.
The benefits of virtual commissioning are accordingly numerous. In addition to the shortening of time and costs associated with commissioning, it enables detailed analysis of the system and testing of its effectiveness, while also providing after-sales or follow-up support with the ability to easily verify any changes over time. In addition, the user-friendly visualization promotes communication and collaboration among the various stakeholders involved in the project and the commissioning.
However, virtual commissioning can also be employed for commercial or marketing purposes. If a demonstration presentation of a plant’s operation is needed, virtual simulations can serve as a convenient preview. This provides a clear and engaging overview.
In addition, the creation of a realistic virtual environment for machine operators and maintenance personnel is possible. Thus, through simulations, employees can enjoy optimal and completely safe training, effectively preparing for their tasks. In addition, tools such as Visual Components can integrate virtual reality into the process, further enhancing the training experience.
Virtual commissioning: the future is now.
Virtual commissioning can arguably be considered a cornerstone practice of advanced automation. Anyone already exploring the Digital Twin can’t help but consider implementing virtual commissioning. Our advice is to use the tools offered by innovative tools such as Visual Components and Flexsim.
In an increasingly digitally driven business world, embracing this methodology means not just staying competitive but also leading the way to a more efficient and innovative future within industrial manufacturing.
Contact Flexcon: find out how to test and refine your real-world manufacturing strategies in a virtual environment.